Contents
What is a Health Passport?
A health passport is a digital or paper document that contains information about an individual's health status. These passports find application in various contexts such as international travel, access to events, and workplace safety, providing a standardized and efficient means to confirm an individual's health credentials while prioritizing privacy and data security.
Few Use Cases of Health Passports
Medical Tourism:
In medical tourism, health passports ensure safe and seamless patient movement across borders. These standardized records, including vaccination history and test results, facilitate efficient entry processes and enhance communication between healthcare systems.

Workplace Safety and Return to Office: Employers can use health passports to track employees' vaccination status or recent test results, enabling a phased and secure return to the office while prioritizing workplace safety.
Healthcare Settings: Health passports streamline access to healthcare facilities, offering quick and secure verification of patients' health status, especially for outpatient visits, elective procedures, and non-emergency services.
Healthcare Networks: Health passports streamline communication across healthcare networks, providing secure access to patients' medical data. This enhances care coordination, ensures timely information for care providers, and contributes to a patient - centric healthcare ecosystem.
Access to Events and Venues: Event organizers can use health passports to ensure that attendees meet certain health criteria, contributing to a safer environment for participants and reducing the risk of disease transmission in crowded settings.
Community Safety Initiatives: Health passports can be used in local communities to facilitate safe gatherings, community events, and activities. This ensures that participants adhere to health guidelines, contributing to the overall well-being of the community.
Emergency Response and Disaster Relief: Health passports assist emergency responders in disaster areas by swiftly verifying individuals' health status, enhancing resource coordination and allocation efficiency.
Educational Institutions: Health passports can be utilized in schools and universities to ensure that students and staff meet health requirements, contributing to a safer learning environment and minimizing the risk of outbreaks.
Some Key Features of Health Passports
Vaccination Records: Information about the individual's vaccination history, including the type of vaccines received and the dates of vaccination.
Test Results and or Health Declarations: Results of recent health tests or declarations that may be relevant to public health, such as symptoms or exposure to infectious diseases.
Health Declarations: Personal health information or declarations that may be relevant to public health, such as symptoms or exposure to infectious diseases.
- Digital Format: Many health passports are digital, stored on a mobile app or other electronic platform, allowing for easy and secure verification.

- Verification Mechanism: Health passports often incorporate a mechanism for verifying the authenticity of the information they contain through secure technologies like blockchain or other cryptographic methods.
Privacy Controls: To address concerns about privacy, some health passports include features that allow individuals to control who can access their health information and for what purposes.
Challenges faced by Health Passports
Here are some key challenges associated with health passports:
Privacy Concerns - Sensitive Information: Health passports involve sharing sensitive health information, raising concerns about potential misuse and emphasizing the need to protect individuals' privacy rights.
Data Security - Cybersecurity Risks: Storing health information digitally creates cybersecurity challenges. Unauthorized access, data breaches, or hacking incidents could compromise the integrity and confidentiality of health passport data.
Equitable Access - Digital Divide: The reliance on digital platforms for health passports may exclude individuals without access to smartphones or digital technologies, potentially exacerbating existing social inequalities.
Standardization and Interoperability - Lack of Standards: The absence of standardized health data formats hampers interoperability among diverse health systems, organizations, and countries, posing a complex challenge in achieving a universal standard for health passports.
- Verification Processes - Reliability: Ensuring reliable and efficient health passport verification poses challenges, demanding coordinated efforts among healthcare providers, testing centers, and government agencies to maintain accurate and up-to-date information.
- Fraud Prevention - Forgery Risks: Health passports may face forgery risks, emphasizing the need for robust mechanisms to prevent fraud and ensure data authenticity.
- Ethical Considerations - Informed Consent: Obtaining informed consent for health data collection is essential, yet ensuring individuals fully comprehend data usage and access remains a challenge in health passport development and deployment.
- Legal and Regulatory Frameworks - Compliance: Health passports must comply with existing data protection laws and regulations. Developing legal frameworks to balance public health needs with individual rights remains an ongoing challenge.
Public Trust and Acceptance - Communication and Education: Building public trust in the security and reliability of health passports is crucial. Effective communication and education about the purpose, benefits, and safeguards in place are essential for widespread acceptance.
Addressing these challenges requires a multidisciplinary approach involving technology experts, policymakers, healthcare professionals, and the public. Striking the right balance between public health objectives and individual rights is key to the successful and ethical implementation of health passports.
Role of Blockchain in Health Passports
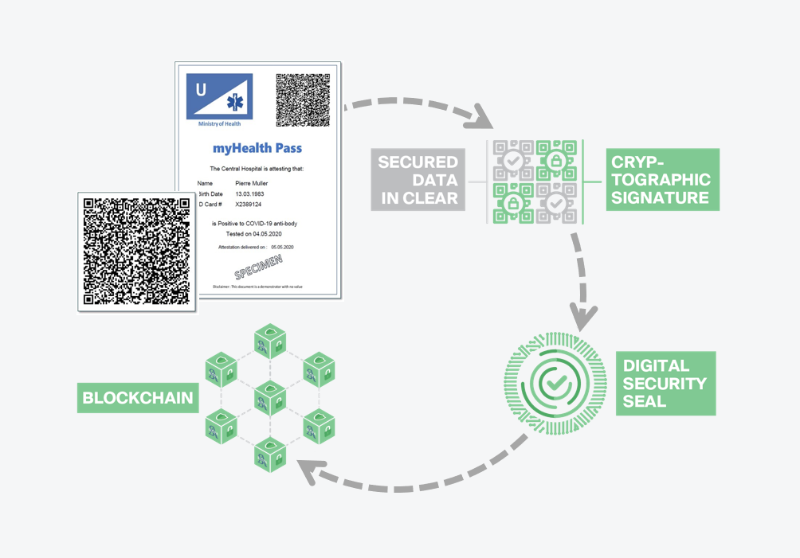
Blockchain plays a crucial role in the implementation of health passports by addressing key challenges related to security, privacy, and the integrity of health data. Here are several ways in which blockchain technology contributes to the development and effectiveness of health passports:
- Data Integrity - Immutable Audit Trail: The blockchain's transparent and immutable audit trail is crucial for ensuring the integrity of health records, establishing trust in the accuracy and reliability of information presented in a health passport. Tokenize by Chainize provides an easy to deploy solution.
Interoperability - Data Standardization: Blockchain enables health data standardization, enhancing interoperability between healthcare systems and organizations, a crucial factor for widespread acceptance and adoption of health passports.
Verification and Authenticity - Secure Verification: Blockchain ensures a secure and transparent verification process for health information authenticity. When a health passport is presented, the blockchain swiftly confirms data integrity.
Privacy Protection - Selective Disclosure: Blockchain enables selective disclosure, allowing individuals to share specific health information without revealing their entire medical history. This enhances privacy by disclosing only necessary information for a particular purpose.
Consent Management - Smart Contracts: Blockchain integrates smart contracts for automated consent processes, executing predefined rules to grant access to health information only under specified conditions.
Global Accessibility - Decentralized Nature: Blockchain's decentralized network enables secure global access to health passport data, especially beneficial for international travel, ensuring availability and verification of health information across borders.
Conclusion
In conclusion, blockchain plays a vital role in health passports, providing solutions to challenges in secure and efficient health information management. Its contributions include enhancing security, privacy, and data integrity in the development of health passports.
While blockchain addresses health passport challenges, its implementation demands careful consideration of regulations, ethics, and stakeholder collaboration. Balancing public health needs and individual privacy rights is crucial for responsible deployment. Continued advancements and adherence to best practices will maximize blockchain's potential in enhancing health passport effectiveness and reliability.
For more information and other Enterprise use cases, contact Chainize.


