Contents
- What is Network Security?
- What is the importance of Network Security?
- Data Protection
- Preventing Cyber Threats
- Business Continuity
- Regulatory Compliance
- Protecting Intellectual Property
- Building Trust
- Addressing Insider Threats
- Critical Infrastructure Protection
- Global Connectivity
- What is Cryptographic Integrity?
- What is Cryptographic Integrity in Network Security?
- Why is Cryptographic Integrity crucial for Network Security?
- Benefits of Cryptographic Integrity in Network Security
- Data Confidentiality
- Data Integrity
- Authentication
- Non-Repudiation
- Secure Communication
- Trust Establishment
- Public Key Encryption
- Protection Against Insider Threats
- Conclusion
What is Network Security?
Network security encompasses a range of measures designed to safeguard computer networks and their resources against unauthorized access, cyberattacks, and data breaches. It involves deploying a blend of technologies, processes, and policies to preserve the confidentiality, integrity, and availability of network assets, establishing a secure and trusted digital ecosystem for seamless data exchange and communication.

What is the importance of Network Security?
The importance of network security lies in its role as a fundamental pillar of cybersecurity. It plays a crucial role in protecting computer networks and the data they transmit from a wide range of threats, including cyberattacks, data breaches, and unauthorized access. The significance of network security can be summarized as follows:
Data Protection
Network security safeguards sensitive and confidential data from unauthorized access, ensuring that only authorized users can access and modify the information.
Preventing Cyber Threats
Network security measures, such as firewalls, intrusion detection systems, SIEM, Antivirus software etc., help detect and prevent cyber threats like malware, ransomware, and phishing attacks, minimizing the risk of data loss and disruption.

Business Continuity
Network security ensures the continuous and uninterrupted operation of networks and critical systems, mitigating the impact of cyber incidents and preventing downtime that could result in financial losses and reputational damage.
Regulatory Compliance
Many industries and regions have strict data privacy regulations that require organizations to implement robust network security measures to protect customer information and maintain compliance.
Protecting Intellectual Property
Network security safeguards valuable intellectual property and trade secrets from theft and unauthorized disclosure, preserving a competitive edge for businesses.

Critical Infrastructure Protection
In sectors like utilities, healthcare, and transportation, network security is vital for protecting critical infrastructure from cyberattacks that could have far-reaching consequences on public safety and essential services.
Global Connectivity
As organizations and individuals become increasingly interconnected through the internet, network security becomes even more crucial to safeguard data and communications across geographically dispersed networks.
In summary, the importance of network security is multifaceted, encompassing data protection, threat prevention, business continuity, regulatory compliance, trust-building, and the safeguarding of critical infrastructure. It is an essential component of modern cybersecurity strategies to protect sensitive information, prevent financial losses, and maintain the integrity and stability of digital operations.
What is Cryptographic Integrity?
Cryptographic integrity refers to the assurance that data remains unaltered and unchanged during transmission, storage, or processing. It is a crucial aspect of data security that ensures the authenticity and reliability of information in various digital systems. Cryptographic integrity mechanisms use mathematical algorithms and hashing techniques to generate a unique cryptographic hash (a fixed-size string of characters) from the original data. By comparing the hash value at the receiving end with the original hash value, one can verify if the data has remained intact and unmodified during its journey, helping detect any unauthorized changes or tampering.

Why is Cryptographic Integrity crucial for Network Security?
The significance of cryptographic integrity in network security cannot be overstated, as it guarantees the dependability and credibility of data and communications within the network. Without robust cryptographic integrity measures, sensitive information transmitted or stored becomes susceptible to unauthorized access, tampering, and eavesdropping.
To fortify the network's security, network administrators can employ cryptographic techniques like encryption, digital signatures, hashing and Tokenization. These measures ensure data confidentiality, verify message authenticity, and enable the detection of any unauthorized alterations, thus reinforcing the overall security posture of the network.
Benefits of Cryptographic Integrity in Network Security
Here are some of the benefits of cryptographic integrity in network security:
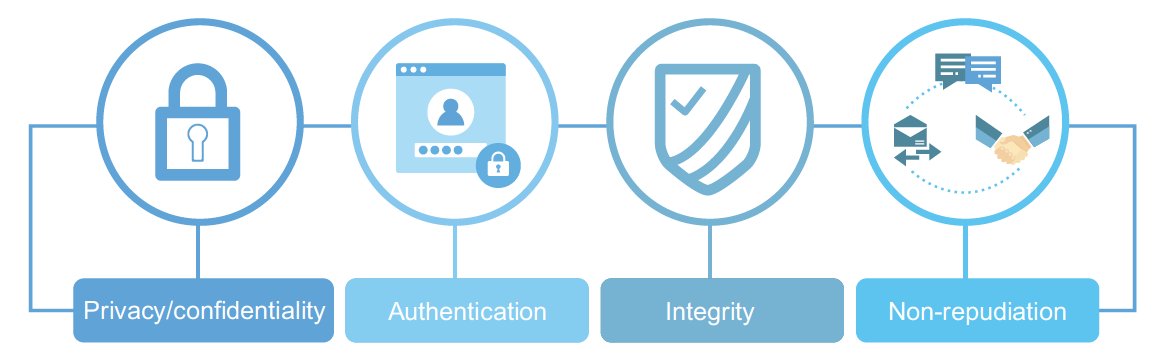
Data Integrity
Cryptographic hashing and digital signatures uphold data integrity, ensuring data remains unchanged during transmission or storage. Hash functions generate unique, fixed-length hashes for data, with any alterations yielding distinct hash values that swiftly alert network administrators to potential tampering efforts. However, the current percentage of verifiable data at rest using Digital Signatures is virtually negligible.
Rather than solely securing data in motion, the potential lies in shaping a new Internet where every data fragment, from log file events to network device configuration files, can be Tokenized. Similar to digital signatures, data can possess cryptographically verifiable attributes like integrity, time, origin, and identity, all without reliance on centralized trust authorities. AssetVigil by Chainize provides an easy to deploy solution.

Non-Repudiation
Cryptographic integrity ensures non-repudiation, where the sender cannot deny their role or the data's authenticity. Tokenization guarantees the confirmation of message or transaction origin and integrity, playing a crucial role in establishing accountability and resolving disputes.

Trust Establishment
Leveraging Tokenization with Blockchain, cryptographic integrity fosters the establishment of trust within network participants. This ensures the validation of entities' legitimacy and identity, forming a web of trust that reduces the likelihood of engagement with malicious entities or unauthorized individuals.
Protection Against Insider Threats

Cryptographic integrity also serves as protection against insider threats. Even within a network, instances of unauthorized access by employees or individuals with malicious intent can be swiftly detected, almost in real time, contrasting with the industry norm of several months' dwell time.
Conclusion
In conclusion, cryptographic integrity plays a pivotal role in upholding the confidentiality, integrity, and authenticity of data and communications within a network. Its advantages are indispensable in protecting sensitive information, thwarting unauthorized access, and preserving the overall security and reliability of networks amidst ever-evolving cybersecurity challenges. For more information and other Enterprise use cases, contact Chainize.


